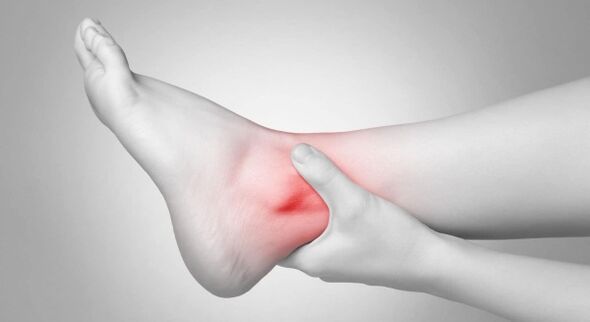
Twelve percent of residents suffer from joint disease, and the condition is more common in women of retirement age.
type
- Cause of occurrence (primary, secondary);
- stages of arthrosis;
- Pathological localization;
- forms of localization (generalized and local);
- Course of disease (acute and chronic).
| Classification criteria | Types of Arthropathy |
|---|---|
| place of performance | Knee, wrist, ankle, elbow, shoulder and neck joints. |
| cause |
|
| localization |
|
| Course of disease |
|
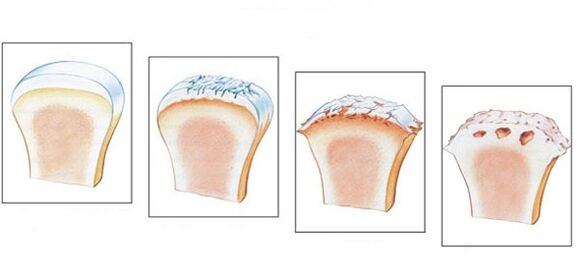
Stages and degrees
- The first stage is often overlooked. Main symptoms: Stiffness in the morning and a characteristic crunching sound when walking. The images do not show pathogenic changes; the destructive process has already begun.
- Morning stiffness can last longer. Leg development takes 20-30 minutes. Some patients develop lameness. On an X-ray, you can see stage 2 pathology through bone growth and bone displacement.
- In the third stage, symptoms become more pronounced. The painful feeling occurs in a calm state, and the patient cannot do without painkillers. Lameness becomes noticeable, sometimes requiring crutches. Joints swell and change, and muscles become thinner and lose volume. Narrowing of the joint space and the formation of osteophytes can be seen on radiographs.
- The final stage occurs without treatment. The cartilage is destroyed and the joint surfaces grow together. The patient cannot walk.
- first level– X-rays did not show any changes or joints. There is slight morning stiffness. At this stage it is necessary to start treatment.
- in the second degreeActivities become difficult, a crunching sound is heard when walking, swelling is observed. X-rays show a narrowing of the joint space. The person will limp and morning stiffness will last longer.
- in the third degreeObvious joint disease of the foot and joint deformation. Muscles atrophy more severely and movement becomes limited. Continuous rest is required. Even in this state the pain does not go away.
- in last degreeThere is almost no joint space and movement is almost impossible. X-rays allow you to diagnose large osteophytes. Only surgical intervention is prescribed.
symptom
- The pain is initially moderate and occurs only with physical activity. The pain may become more severe over time and bother you at rest;
- When injured and dislocated, swelling and inflammation appear, and the temperature of the injured area increases;
- "Dry" clicking sound accompanied by pain;
- Dislocation, in which the joint loses stability as the cartilage tissue thins and degrades. Bones shift and become detached from the joint capsule;
- joint stiffness;
- When walking, one quickly becomes tired;
- In the final stage, the joint deforms.
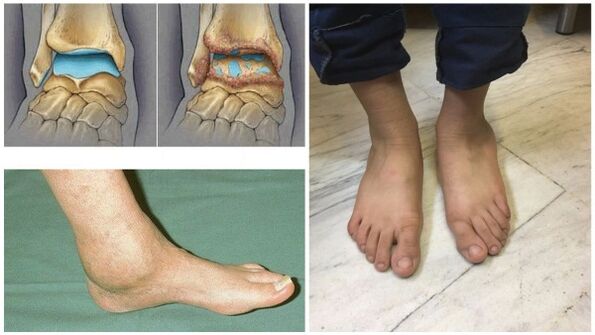
Reason for occurrence
- Injuries, dislocations and bruises;
- age-related joint and ligament disorders;
- inflammatory process;
- overweight;
- disrupt metabolic processes;
- Congenital foot deformities and flat feet that appear during life;
- genetic predisposition;
- excessive physical activity;
- using uncomfortable shoes;
- Endocrine system diseases;
- Osteochondrosis.

diagnosis
- simpleradiographyis the most reliable method. Muscles do not perceive X-rays equally: soft muscles transmit X-rays, while hard muscles absorb them. The study sheds light on the disease itself and its consequences.
This image allows you to analyze the condition of the bone surfaces in the joint, the shape, size, and position of structures relative to each other, the condition of the tissues, and the size of the joint space. From these data, the extent of pathology can be determined. 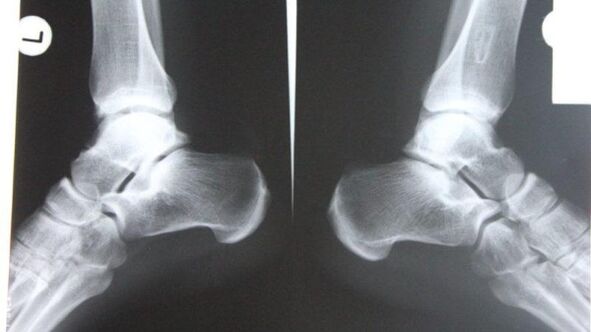
If the ankle joint is affected, diagnosis is made by the lateral, posterior, and posterior projections of the foot moving inward. If corresponding symptoms (signs such as joint space narrowing, osteophytes, etc. ) occur, joint disease can be diagnosed. - NMRDetermining the disruption of hydrogen molecule functionality under the influence of strong magnetic fields. Allows you to explore hydrated areas of your body.
The darker shades in the image represent bones because they contain much less water, while muscles, nerves, and discs appear lighter. Diagnosis can reveal even minor disorders of bone tissue and joints. This procedure is indicated before joint replacement. The only drawback is the higher cost of diagnosis. - Magnetic resonance imagingVery accurately examines the ligamentous structure, muscle tissue and cartilage of the joint. Through this study, experts can evaluate the condition of the lower leg joints, allowing the identification of pathology at the earliest stages of its development. The procedure is painless and lasts about 30 minutes.
During surgery, radio waves and strong magnetic radiation can affect people. It must be remembered that magnetic fields are dangerous for physiological states. MRI is contraindicated if you have a neuropsychiatric disorder, are pregnant, or have metal objects in your body. - ultrasoundAccurate diagnosis can be made. The device generates waves that are reflected by the tissue and recorded on the screen. The doctor examines the image and makes a diagnosis. For a clear image, use gel to remove air and ensure easy movement on the surface.
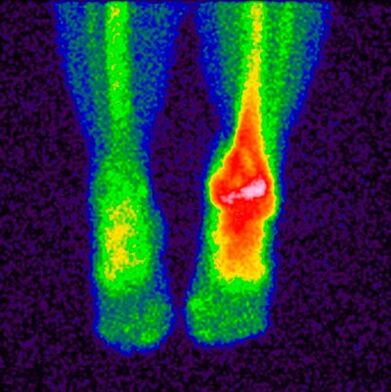
The advantages of this surgery are health, safety, affordability, and high accuracy. - bone scintigraphy– A study that allows the use of isotopes to determine pathological diseases of the bones. A special substance containing labeled atoms is injected into the patient. Pathological areas are divided into cold areas and hot areas.
The first has no isotopes, blood flow to them is poor, and they cannot be detected during scanning. This includes sites where malignant tumors have occurred. In hotspot areas, isotope collection is more active and can be clearly detected during scanning. These areas indicate the occurrence of inflammatory processes. This study makes it possible to distinguish arthropathy from similar diseases with similar clinical symptoms; based on the results, doctors make a prognosis and formulate a treatment plan. The main contraindications to the study are pregnancy, breastfeeding, and taking barium-containing medications. - joint punctureIt is a procedure in which a doctor inserts a needle into a joint cavity to draw synovial fluid for analysis.
Research on this biological material will continue in the future; based on the results, experts determine the characteristics of the disease and its stages of development. For the ankle joint, the puncture is performed anteriorly between the lateral malleolus and the extensor digitorum longus tendon.
When to see a doctor
- Discomfort and pain in joints after overloading at the end of a working day;
- It’s hard to find a comfortable position for your legs at night;
- The joints swell and the skin becomes red;
- Severe pain and difficulty moving;
- A crunching sound occurs;
- Joint deformation.
prevention
- Wear shoes that fit comfortably without high heels;
- Maintain proper nutrition and drink enough clean water;
- Choose the right vitamin and mineral complex;
- exercise;
- Take frequent walks in the fresh air;
- Avoid putting excessive pressure on your legs;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Undertake regular observation by a doctor;
- Get rid of bad habits;
- Do a set of exercises to warm up your ankle joints.

- You need to eat small amounts often.
- Drink at least 2 liters of clean water.
- Avoid sweet and salty foods.
- Don't eat 4 hours before going to bed.
- Steam, bake, and boil food.
Patients with joint disease are strictly prohibited from fasting and eating a strict diet to prevent the loss of calcium needed for bone and cartilage recovery.
treatment method
drug
- Anti-inflammatory (medicine)Painkillers remove the source of inflammation and relieve pain. Use tablets and ointments. The sooner you take anti-inflammatory medications, the better your chances of saving your joints.
- GlucocorticoidsUse if the above medications do not have the desired effect. They are produced as injectable solutions and injected into the joints.
- chondroprotectantNecessary to slow down the process of cartilage destruction.
traditional method
- Wash the burdock leaves thoroughly and apply them to the skin with the soft side. Secure the plant with a bandage or plastic wrap and leave overnight.
- Heat sea salt (buckwheat, sand) in a frying pan, pour it into a linen cloth and apply it to the sore area. Keep until the salt is cold. This is an effective way to relieve pain.
- Pour triple cologne over lilac and leave it in a dark place for two weeks, rubbing the sore area twice a day.
- Grind the eggshells into powder and take 0. 5 teaspoons. before eating.

Other methods
- Repetitive and primary joints 3-4 degrees;
- complication;
- Severe and persistent pain radiating to the knee;
- Marked limp;
- Paralysis of leg muscles;
- The flexion and extension performance of the joints and the support ability of the foot deteriorate.
- Arthrodesis– Surgery to stabilize the joint. Its job is to restore the lost ability to support the limb. The main disadvantage is that the bones may fuse together, resulting in immobility, so they are rarely used.
- ArthroscopyIt is a minimally invasive procedure in which the doctor cuts into the joint and inserts an arthroscope. The surgeon performs a visual inspection and evaluates the condition of the structures within the joint and, if necessary, removes part of the damaged joint or blood clots in the synovial fluid. The risk of recurrence with this surgery is too high.
- endoprosthesisIn particularly serious cases. Allows partial or complete replacement of damaged joints. Prostheses with modern mechanics have a service life of up to 20 years.
possible complications
- Disability;
- irreversible deformation;
- Inactivity and immobility of joints;
- Quality and standard of life decline.